Insights
Articles
3 December 2025
7 min read
AV/VR Meets Enterprise: How Entertainment-Grade Tech Is Shaping Business Infrastructure.
Praise Ohans
Author

Introduction
When you hear “AV and VR”, what first comes to mind is the entertainment world, especially gaming tournaments and blockbuster visuals, and rightly so. Well, the same technology is now moving directly into the heart of enterprise operations. Companies are realizing that immersive tools can solve real business problems in ways traditional screens cannot match.
Market signals highlight this adoption perfectly. The global AR and VR market is on track to hit $62 billion by 2029. With this kind of projected growth, it is safe to infer that immersive technology is becoming an integral part of core business infrastructure. This adoption will only result in a new era where teams train faster, and collaborate more effectively. AV and VR help companies reduce risk, speed up development, and unlock new levels of productivity.
From Gaming Headsets to Enterprise Hardware
The early versions of AR and VR devices were designed mainly for consumer entertainment. Today, the hardware has evolved into systems built for professional environments. These devices now support advanced optics, high resolution displays, mixed reality capabilities, and secure enterprise features.
Meta Quest 3 and Quest Pro are two of the clearest examples of this modernization. They started in the consumer space but are now being widely used in healthcare, aviation, manufacturing, and field operations. The Quest 3 enables full color passthrough and accurate room mapping, which makes it ideal for industrial settings where workers must see both digital instructions and real equipment.
Apple Vision Pro has gone even deeper into enterprise workflows. It offers high fidelity displays that support detailed work such as surgical planning, mechanical assembly, or design reviews. Fortune 500 companies already use it for collaboration and spatial analysis, proving that spatial computing is moving into the mainstream.
Enterprise interest is skyrocketing, with 67% of businesses considering AR for future use. This level of adoption has pushed hardware makers to add features that enterprises depend on. Examples include device management tools, compliance controls, enterprise identity support, and improved security protocols.
Digital Twins
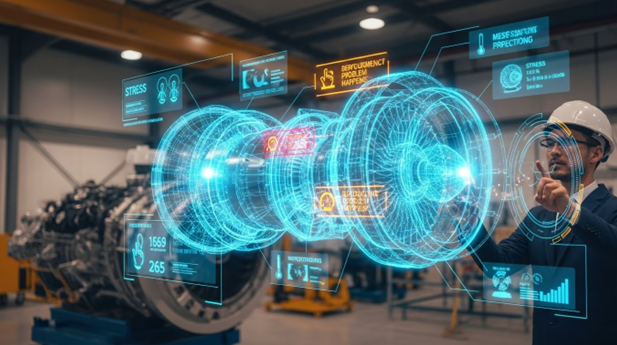
A digital twin is a virtual version of a real asset, process, or system. It may look like a simple idea on the surface, but it is becoming one of the most important tools in modern enterprise planning. A digital twin lets teams test ideas, predict outcomes, and fix problems before real world implementation. This reduces risk, cuts costs, and allows for better decision making.
Large enterprises are already using digital twins on a serious scale. KLM Royal Dutch Airlines uses the Engine Shop app on Apple Vision Pro to train technicians on detailed engine models. This reduces the need to take aircraft offline and makes training faster and safer. Mortenson, a leader in data center construction, used digital twins to run virtual inspections across teams in four different states. They identified more than six hundred issues before construction even started. Fixing only one of those issues saved over $26,000.
The market reflects the importance of this technology. Research suggests the global digital twin market could reach $155.84 billion by 2030. It is clear that digital twins technology is essential for future growth of companies, hence the wide adoption globally.
Immersive Training
Immersive Training has to be one of the strongest use cases for VR right now. Immersive learning helps people master skills faster, remember information longer, and avoid the risks that come with real world training. With VR, teams can now learn by doing inside a realistic virtual environment. Training time drops sharply with VR. Some task based roles see reductions of up to 65%. Skill development is also four times faster compared to traditional training. When you scale this across hundreds or thousands of employees, the value becomes clear.
Meta’s research shows how big the impact can be. A 2025 Forrester study commissioned by Meta found out that companies using Meta Quest headsets recorded a return on investment of 219% over three years. That equals more than $6.1 million in benefits. The investment paid for itself in less than six months, which is rare for most enterprise technology.
Pfizer used VR to train operators during the global rush to produce the COVID-19 vaccine. They built a complete digital twin of the production environment and deployed more than 500 Meta Quest devices across multiple countries. Workers practiced aseptic techniques with haptic feedback and hand tracking, which created a realistic and safe learning experience.
Immersive training has become a reliable way to build skills at scale. It saves time, reduces risk, and helps companies train global teams with consistent quality. It is one of the clearest examples of how AV and VR are becoming essential to enterprise operations.
Spatial computing
With spatial computing, the digital workspace is changing from flat screens to fully interactive 3D environments. Instead of having to click through windows on a laptop, teams can manipulate life-sized models, pin dashboards around a room, and collaborate inside virtual spaces that feel natural. This upgrade is making work faster, clearer, and way more immersive.
Design teams are already taking advantage of this shift using Vision Pro. With the Onshape Vision app, product designers can open full CAD models in front of them, walk around them, and review components in real time during design meetings. This eliminates the need for multiple physical prototypes and helps teams speed up decisions with fewer revisions.
Collaboration is evolving as well. Microsoft’s partnership with Meta brings Microsoft 365 apps and Microsoft Mesh to Quest headsets. Teams can meet in shared spatial workspaces where documents, models, and whiteboards appear around them. Hand tracking and haptic feedback makes remote work feel even more realistic than face-to-face collaboration. Makes it easier to share ideas and get every team member up to speed faster than traditional brainstorming sessions in a shared space.
Industry-Specific Transformations
Healthcare
Healthcare is experiencing a major breakthrough from immersive technology. VR and AR are boosting surgical accuracy, improving training quality, and helping doctors plan complex cases better. Digital twins built from CT scans allow surgeons to walk through procedures before entering the operating room. This results in improved patient outcomes and reduced complications.
Companies like Stryker equip surgeons with Vision Pro to explore surgical plans in high-resolution, immersive environments. This helps teams collaborate around cases, and deliver more consistent results.
Manufacturing and Automotive
Manufacturing and automotive brands are using VR and AR to cut costs, improve design quality, and boost safety. Honda, BMW, and Jaguar Land Rover use VR for design reviews, enabling teams to evaluate engineering changes instantly. This reduces the number of physical prototypes needed and shortens product development cycles.
Digital twins are especially valuable in this sector. Automakers build virtual replicas of car components and production lines to understand how vehicles behave in real conditions. This helps engineers identify safety improvements early, optimize performance, and prevent accidents before they happen.
Energy and Infrastructure
The energy and infrastructure sectors rely heavily on large assets, complex logistics, and constant monitoring. The advent of VR, AR, and digital twins are making this work more predictable and efficient. Companies like Shell and GE Vernova use digital twins to monitor real-time system performance. They analyze weather data, equipment status, and market signals to predict failures and optimize output in real time.
Civil engineers use spatial computing and 3D models to plan infrastructure upgrades. These virtual simulations show how crowds, vehicles, and environmental factors interact with bridges, roads, and public spaces. Testing these designs digitally helps avoid mistakes and ensures safer implementation.
For environmental planning, energy distribution, construction, and city development, digital twins are giving decision-makers a level of foresight they’ve literally never had before.
Conclusion.
Immersive technology has now moved from gaming halls into factories, hospitals, and energy plants,gradually changing how modern enterprises work. AV, VR, and spatial computing now power faster training, clearer collaboration, safer operations, and smarter decision making. The results are already obvious across industries. Companies are cutting training time, reducing errors, and improving planning with digital twins and spatial computing.
Because of the massive impact immersive technology has had across industries, it doesn’t come as a surprise that more organizations are expected to adopt these tools. With time, immersive technology will sit alongside everyday business systems because it is practical, measurable, and shaping how modern enterprises operate.
TAGS:
Build what matters, with Gozade
Let's Talk
Gozade
HOUSE NO. 33C, ROAD 2, IKOTA VILLA ESTATE, IKOTA, LEKKI, LAGOS
+2349032770671, +2349032942619
Gozade builds smart digital solutions that help businesses grow and scale with confidence.

